Traveling Luck for Suriname. Suriname, South America
Suriname is located in Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French Guiana and Guyana.
Land in Suriname is mostly rolling hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps.
Surinamese land covers an area of 163270 square kilometers which is slightly larger than Georgia
Suriname has borders with Brazil for 597km, French Guiana for 510km and Guyana for 600km.
 Surinamese national flag (Flag of Suriname)
Surinamese national flag (Flag of Suriname)
As for the Surinamese climate; tropical; moderated by trade winds.
Surinamer(s) speak Dutch (official), English (widely spoken), Sranang Tongo (Surinamese, sometimes called Taki-Taki, is native language of Creoles and much of the younger population and is lingua franca among others), Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), Javanese.
Places of note in Suriname
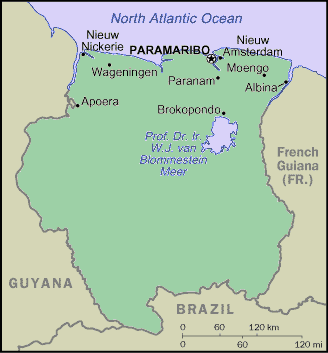 Surinamese map
Surinamese map
Regions of Suriname
Independence from the Netherlands was granted in 1975. Five years later the civilian government was replaced by a military regime that soon declared a socialist republic. It continued to rule through a succession of nominally civilian administrations until 1987, when international pressure finally forced a democratic election. In 1990, the military overthrew the civilian government, but a democratically elected government returned to power in 1991.
The economy is dominated by the mining industry, which accounts for more than a third of GDP and subjects government revenues to mineral price volatility. The short-term economic outlook depends on the government's ability to control inflation and on the development of projects in the bauxite and gold mining sectors. Suriname's economic prospects for the medium term will depend on continued commitment to responsible monetary and fiscal policies and to the introduction of structural reforms to liberalize markets and promote competition. The government of Ronald VENETIAAN, in his first term, implemented an austerity program, raised taxes, and attempted to control spending. Economic policies are likely to remain the same during VENETIAAN's second term. Prospects for local onshore oil production are good, as a drilling program is underway. Offshore oil drilling was given a boost in 2004 when the State Oil Company (Staatsolie) signed exploration agreements with Repsol, Mearsk, and Occidental.
Surinamese natural resources include timber, hydropower, fish, kaolin, shrimp, bauxite, gold, and small amounts of nickel, copper, platinum, iron ore
smallest independent country on South American continent; mostly tropical rain forest; great diversity of flora and fauna that, for the most part, is increasingly threatened by new development; relatively small population, mostly along the coast
Surinamese religion is Hindu 27.4%, Protestant 25.2% (predominantly Moravian), Roman Catholic 22.8%, Muslim 19.6%, indigenous beliefs 5%.
Natural hazards in Suriname include NA.
Travel Advice for Suriname
SurinameSUMMARY
- There is no British High Commission in Suriname. For emergency consular assistance you should telephone the British Honorary Consul (+597 402 558 or +597 402 870). Alternatively, you can contact the British High Commission in Georgetown, Guyana (see Contact details section).
- The threat from terrorism is low.
- Around 700 British tourists/nationals visit Suriname every year. Most visits are trouble-free. We are not aware of any British nationals who have required consular assistance in Suriname in the past year but burglary, armed robbery and violent crime occur with some frequency in Paramaribo and in outlying areas.
- We strongly recommend that you obtain comprehensive travel and medical insurance before travelling. You should check any exclusions, and that your policy covers you for the activities you want to undertake. Please see: Travel Insurance.
SAFETY AND SECURITY
GENERAL
OTHER

 Search
Search Suriname country profile
Suriname country profile Travel advice for Suriname
Travel advice for Suriname